The significance of PD-L1 expression detection
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1, also known as B7-H1) is a ligand for PD-1 and belongs to the B7 superfamily. It plays a role in negative regulation of immune responses. PD-L1 can be expressed by T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It is expressed in various types of tumors, including melanoma, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. Studies have shown that the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway is considered a key molecule mediating immune escape in the tumor microenvironment. Blocking this pathway can relieve the inhibition of tumor cells on T lymphocytes and enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate tumors. Therefore, the expression of PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells is an important predictive biomarker for the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy.
Currently, various anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy drugs have been approved for clinical use, and PD-L1 protein expression detection has been approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and various guidelines worldwide as a biomarker for multiple tumor immunotherapies. It is used to guide the selection of patients for immunotherapy and predict the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Their IHC stainers of CNT 300, CNT 330, and CNT 360 can facilitate the detection of PD-L1.
Sample Types of PD-L1 Detection
The sample types recommended for PD-L1 immunohistochemistry testing currently include histological samples and some cytological samples (such as pleural fluid, ascites, etc.). Quality control generally requires a minimum of 100 tumor cells in the sample. The “Expert Consensus on Immunohistochemical Detection of PD-L1 in Solid Tumors (2021 Edition)” and the “Chinese Expert Consensus on PD-L1 Expression Detection in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (2020 Edition)” summarize the types of samples that can be tested for PD-L1:
- It is recommended to prioritize PD-L1 immunohistochemistry testing in tumor tissue sections from paraffin-embedded specimens, ensuring an adequate number of tumor cells for evaluation. Studies have shown high consistency (94%) in PD-L1 expression rates among multiple tissue blocks from the same tumor in lung cancer patients.
- PD-L1 testing can be performed on both surgical resection specimens and biopsy specimens. If tissue specimens are not available, cytological samples such as pleural or ascitic fluid can be embedded in paraffin blocks for testing.
- Both primary and metastatic lesions can be used for PD-L1 testing. As there may be differences in PD-L1 expression between metastatic and primary lesions, it is recommended to perform PD-L1 testing separately on both types of lesions if necessary to clarify the PD-L1 expression status.
- Due to the temporal heterogeneity and treatment influence on PD-L1 expression, it is recommended to perform PD-L1 testing at the time of initial diagnosis and before changing treatment plans.
- PD-L1 immunohistochemistry testing is not recommended in decalcified specimens.
Challenges in PD-L1 detection
Detection platforms:
Different antibodies require the use of different detection platforms.
Spatial and temporal heterogeneity:
PD-L1 expression may vary at different locations within the same tumor, and the expression may also differ between primary and metastatic lesions. This spatial heterogeneity means that different biopsy sites can yield different PD-L1 expression detection results. Additionally, PD-L1 expression levels can change dynamically over the course of the disease, such as with the use of immunotherapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, anti-angiogenic therapy, etc.
Interpretation of results:
Different antibodies have different interpretation criteria for their detection results. The interpretation methods may also vary for the same antibody in different tumor types. Different companies use different antibodies for PD-L1 testing, and each antibody has its own reference index or threshold criteria. In tumor tissues, in addition to cancer cells, there are also stromal cells (such as immune cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, etc.) surrounding them. Therefore, when staining a tumor tissue sample, the stained cells may include both cancer cells and other cells. The determination methods used for PD-L1 testing antibodies include Tumor Proportion Score (TPS), Combined Positive Score (CPS), and separate calculation of Tumor Cells (TC) and Immune Cells (IC).
These challenges highlight the complexity and variability in PD-L1 detection, requiring careful consideration and standardization of testing protocols and interpretation criteria to ensure accurate and reliable results.
PD-L1 Immunohistochemistry Test Reagents
Currently, there are six PD-L1 companion diagnostic antibodies approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China. These include DAKO’s 22C3 and 28-8, Roche’s SP142 and SP263, Wondfo’s WD160, and AmoyDx’s E1L3N. With their advantages of cost-effectiveness and consistent testing results, domestically produced PD-L1 antibody products are gaining popularity in the market.
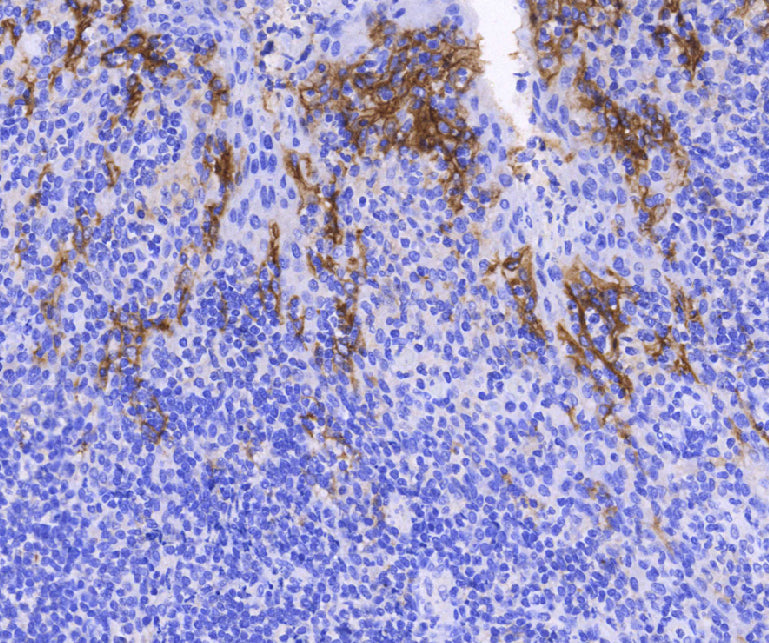
PD-L1(Clone: E1L3N)
E1L3N, the first domestically produced PD-L1 companion diagnostic product, is used as a companion diagnostic for the internationally renowned immunotherapy drugs pembrolizumab (trade name: Keytruda) and nivolumab (trade name: Opdivo) in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. International studies have shown good consistency between the E1L3N clone and the 22C3, 28-8, and SP263 antibodies in detecting PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. The staining pattern and intensity are similar to SP263, and it has better sensitivity than the SP142 clone, especially in cases of low PD-L1 expression.
Platform adaptability is another advantage of E1L3N. It can be used on multiple detection platforms, as it has been extensively validated on the Celnovte platform with good consistency. This facilitates the widespread use of PD-L1 testing in hospitals, benefiting a large number of cancer patients.
E1L3N, as a representative domestically produced reagent for immune therapy companion diagnostics, has received priority recommendation in the Chinese Expert Consensus on PD-L1 Expression Detection in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (2023 Edition).
PD-L1 Detecting Solutions of Celnovte
Celnovte Biotech, established in 2010, is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the research, development, production, and sales of precision diagnostic instruments and reagents for tumors. With a strong focus on quality and innovation, the company has established a comprehensive system that complies with GMP requirements, including production, quality control, and research and development. Celnovte Biotech possesses clean production workshops and state-of-the-art equipment, ensuring the highest standards in their products. The company has obtained ISO9001, ISO13485, and EU CE-ID certifications, positioning itself as a leader in the industry. Guided by their business philosophy of quality, innovation, and service, Celnovte Biotech is dedicated to providing top-notch products and services to its users. They aim to become a benchmark technology innovation enterprise in the industry, contributing to scientific and technological advancements in the field of life sciences and medicine. With a focus on early screening, precise diagnosis, drug companion, and treatment monitoring of tumors, Celnovte Biotech strives to build a complete industrial chain, integrating research and development, production, sales, and service. Their goal is to become a leading provider of comprehensive solutions for tumor pathology diagnosis products, both domestically and internationally.

Celnovte Antibody R&D Center provides a complete PD-L1 detecting solution, including PD-L1 antibody reagents (clone: E1L3N), secondary antibody detection systems, and immunohistochemistry staining platforms, supporting immune therapy companion diagnostics. Their IHC stainers of CNT300, CNT330, and CNT360 are efficient solutions for detection and diagnosis.